business sectors concerned
Gaseous carburizing and carbonitriding are widely used for mechanical parts subjected to fatigue and friction (wear resistance and seizure).
Our various documentations
Our FAQs
Diffuse carbon (carbon and nitrogen in the case of carbonitriding) on the surface of the part, to considerably improve the part's mechanical strength and wear resistance on the surface, while maintaining good core strength.
It's an operation that modifies the internal structure of an alloy to change its properties. In general, there are 3 phases: heating, holding at temperature and slow or rapid cooling (in this case called quenching).
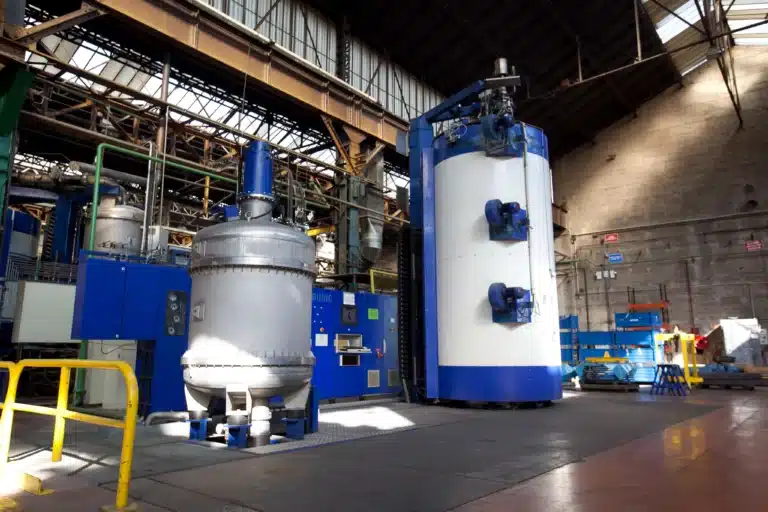
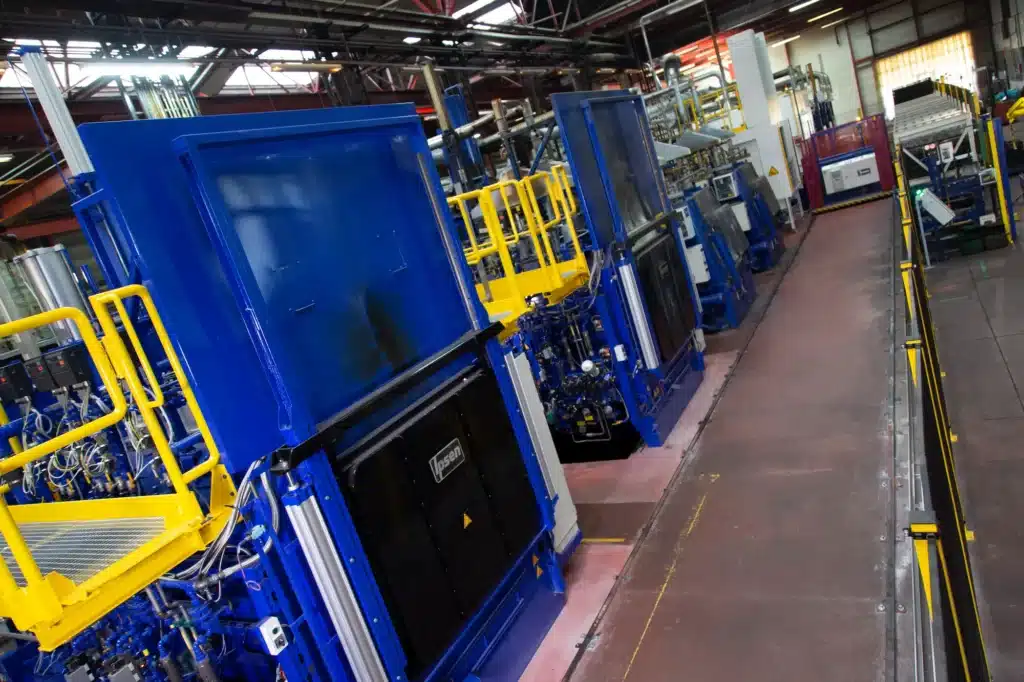
Atmospheric heat treatment enables the use of low-cost steels. Atmospheric technologies are ideal for large-scale production runs and large dimensions.
Heat treatment reveals different levels of stress from previous stages (manufacturing). These stress relaxations can lead to deformations that must be anticipated at the time of machining. In the case of heat treatment in the mass (quenching, tempering), these extra thicknesses depend on the dimensions of the part, but are of the order of a few tenths to 1 mm.
To limit the level of deformation, it is advisable to carry out a stabilization treatment on the blank.